Hypertension – Early Symptoms and Risk Factors
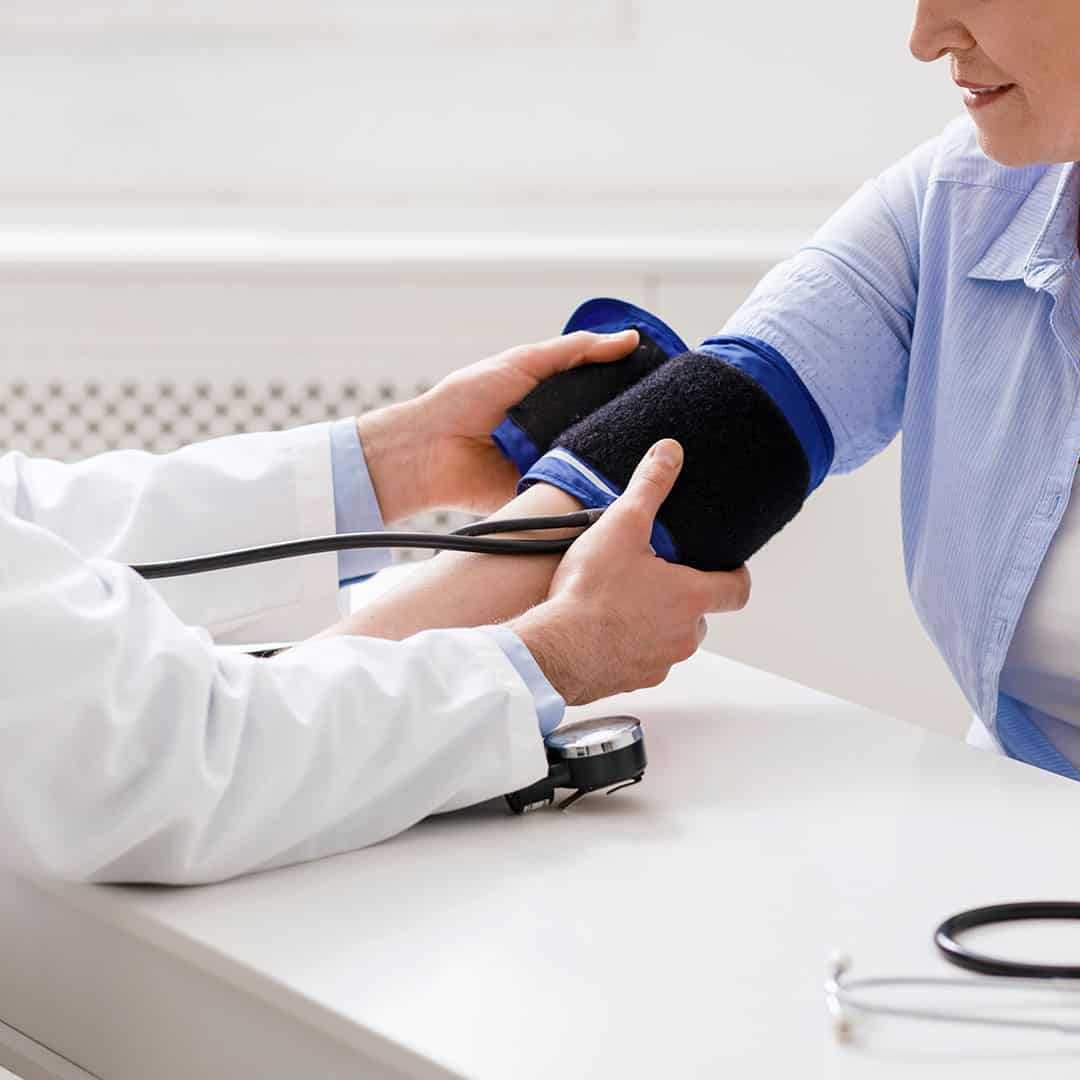
Hypertension or high blood pressure disease is a term used for blood pressure levels above 140/90 mmHg according to JNC 8 criteria. In order for a person to be diagnosed with hypertension, a level above 140/90 must be detected in measurements taken at least twice (on different days).
Yüksek tansiyon birinci ve ikincil olarak iki kategoriye ayrılır. Birinci (primer) hipertansiyon, sebebi bilinmeyen veya bulunamayan hipertansiyon vakaları için kullanılan genel bir addır. İkincil hipertansiyon ise bilinen başka bir rahatsızlıktan dolayı yüksek tansiyon görülmesi ile alakalıdır. Hipertansiyon vakalarının neredeyse %95’i primer tansiyon olarak kategorize edilir.
Hypertension is a disorder that can progress silently and insidiously until it causes organ damage. While some people may not know they have hypertension until they experience organ damage, some people may experience early symptoms. Early symptoms of hypertension include:
- Headache
– Dizziness
– Tinnitus
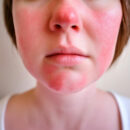
– Facial redness
- Nose bleeding
– Fatigue and sleep disorders
– There is chest discomfort and palpitations.
Not all symptoms may be present in every hypertension patient. Therefore, it is very important for people who have a family history of hypertension to have their blood pressure measured at regular intervals. In general, people at risk for hypertension and their risk factors can be categorized as follows:
– Having hypertension in the family
– Advanced age
- Obesity
– Diabetes
– Smoking, alcohol and caffeine use
– A diet rich in sodium and poor in potassium
– Physical inactivity
– Stress
Stroke, kidney damage, eye disorders and heart attack due to hypertension are frequently encountered and undesirable diseases. As we mentioned before, while high blood pressure sometimes shows early symptoms, it can sometimes cause organ damage without showing any symptoms. In order to avoid such problems, blood pressure should be measured regularly and necessary precautions should be taken when faced with a possible hypertension condition.
In people with hypertension problems, if the blood pressure is not too high, a solution can be provided without the use of medication by making lifestyle changes in the first place. It may be possible to prevent the problem of hypertension before it escalates, without the need for medication, by taking measures such as reducing the amount of salt in meals, increasing the consumption of potassium-containing foods, losing weight, exercising, reducing alcohol and quitting smoking.
If the person has difficulty making lifestyle changes or if the problem persists despite these changes, then anti-hypertensive drug treatments should be arranged. Medication selection will vary depending on the person's age, existing chronic diseases, pregnancy status and ethnicity, so do not use medication for blood pressure control without consulting your doctor.