Knee Arthritis
Arthritis; It is inflammation of one or more of your joints. Pain, swelling and stiffness are the main symptoms of arthritis. While any joint in the body can be affected by this disease, it is especially common in the knees.
Knee arthritis can make it difficult to do many daily activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. This is a major cause of lost work time and serious disability for many people.
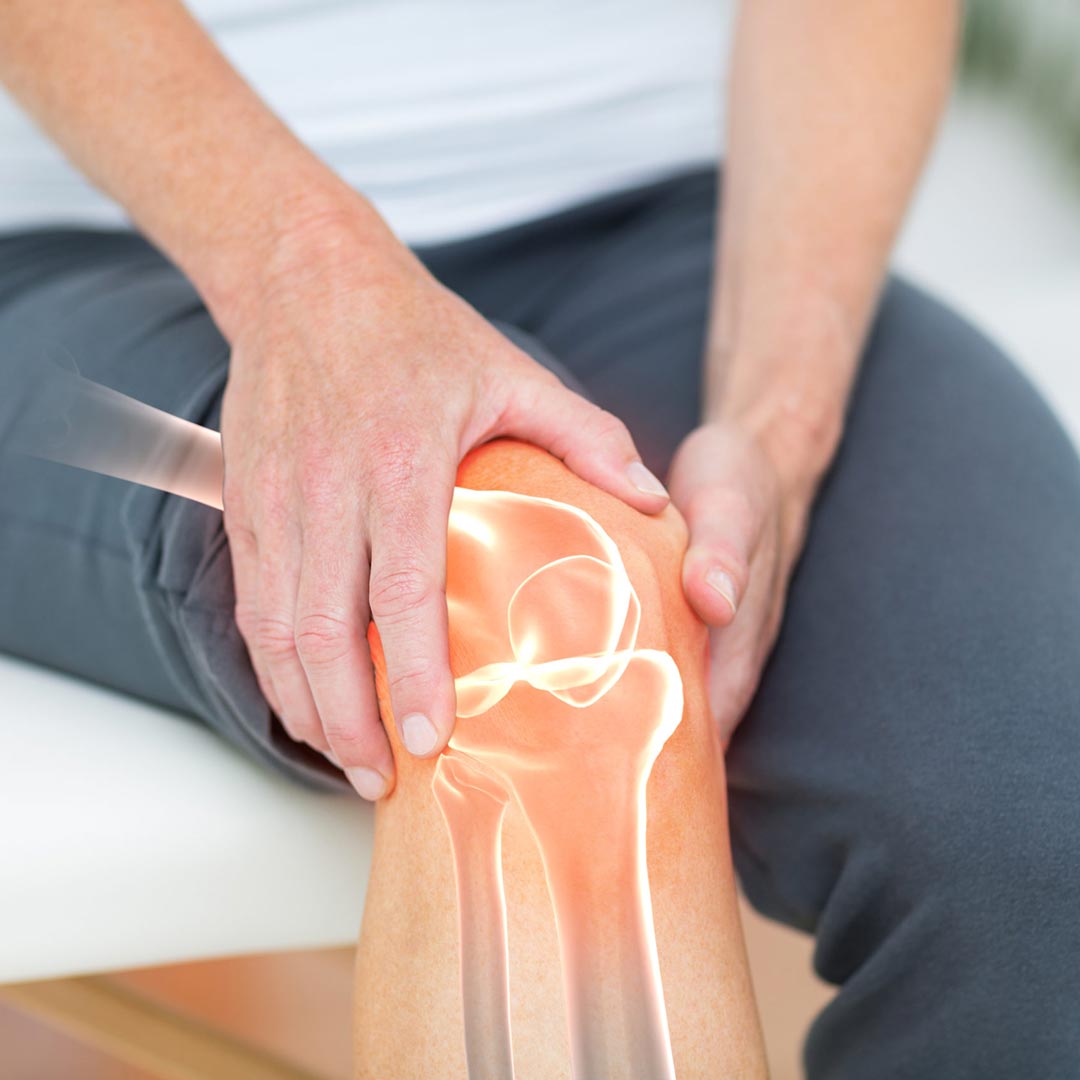
The knee is the largest and strongest joint in your body. It consists of the lower end of the femur (thigh bone), the upper end of the tibia (shinbone) and the patella (kneecap). The ends of the three bones that make up the knee joint are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth, slippery substance that protects and cushions the bones as you bend and straighten your knee.
Two wedge-shaped pieces of cartilage called menisci act as “shock absorbers” between your femur and shin bone. It has a tough and elastic structure to help cushion the joint and keep it stable.
The knee joint is surrounded by a thin lining called the synovial membrane. This membrane produces a fluid that lubricates the cartilage and reduces friction.
The main types of arthritis affecting the knee are;
Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Posttraumatic Arthritis.
OSTEOARTHRITIS: It is the most common form of arthritis in the knee. It is a degenerative (wear-and-tear) type of arthritis that is most commonly seen in people aged 50 and over, although it can also occur in younger people.
In osteoarthritis, the cartilage in the knee joint gradually wears away. As cartilage wears out, it hardens and the protective space between bones decreases. Over time, it can cause bone to rub against bone and cause painful bone spurs.
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: It is a chronic disease that affects multiple joints in the body, including the knee joint. It is symmetrical, meaning it usually affects the same joint on both sides of the body.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the synovial membrane covering the knee joint begins to swell, causing knee pain and stiffness.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means that the immune system attacks its own tissues. The immune system damages normal tissue (such as cartilage and ligaments) and softens bone.
POST-TRAUMATIC ARTHRITIS: Post-traumatic arthritis is a form of arthritis that develops after an injury to the knee. For example, a fractured bone that develops can damage the joint surface and cause arthritis years after the injury. Meniscus tears and ligament injuries can cause laxity and additional wear on the knee joint, which can lead to arthritis over time.
SYMPTOMS:
- A knee joint affected by arthritis can be painful and inflamed. Usually the pain develops gradually over time, but sudden onset is also possible.
- The joint may become stiff and swollen. This can make it difficult to bend and straighten the knee.
- Pain and swelling may be worse in the morning or after sitting or resting.
- Vigorous activity may cause the pain to flare up.
- Loose pieces of cartilage and other tissues can prevent proper movement of joints. The knee may “lock” or “jam” during movement.
- The pain may cause a feeling of weakness or sprain in the knee.
- Many people with arthritis find that their joint pain increases with changes in weather conditions.
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENT:
As with other arthritic conditions, the initial treatment for knee arthritis is nonsurgical. Your doctor may recommend a number of treatment options.
Lifestyle Changes:
Some changes in your daily life can protect your knee joint and slow the progression of arthritis.
- Minimize activities that aggravate the condition, such as climbing stairs.
- Switching from high-impact activities (like running or tennis) to lower-impact activities (like swimming or cycling) will put less stress on your knee.
- Losing weight can reduce stress on the knee joint. This results in less pain and greater function.
Physiotheraphy:
Specific exercises can help strengthen the muscles in your leg, as well as increase movement and flexibility. Your doctor or a physical therapist can help you develop a personalized exercise program that meets your needs and lifestyle.
Auxiliary devices:
Using devices such as a cane and shock-absorbing shoes or wearing a brace may help.
Medicines:
Various types of medications are useful in treating knee arthritis. Because people respond differently to medications, your doctor will work closely with you to determine medications and dosages that are safe and effective for you.
Over-the-counter, non-narcotic pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications are often the first treatment option for knee arthritis. Acetaminophen is a simple, over-the-counter pain reliever that can be effective in reducing arthritis pain.
Like all medications, over-the-counter pain relievers can cause side effects and interact with other medications you are taking. Be sure to discuss possible side effects with your doctor.
Corticosteroids (also known as cortisone) are powerful anti-inflammatory substances that can be injected into the joint. These injections provide pain relief and reduce inflammation; but the effects do not last forever. Your doctor may recommend limiting the number of injections to three or four per joint per year due to possible side effects. In some cases, pain and swelling may “flare up” immediately after injection, and the potential for long-term joint damage or infection exists. With frequently repeated injections or injections over a long period of time, joint damage may actually increase rather than decrease.
Viscosupplementation; It involves injecting substances into the joint to improve the quality of joint fluid.
Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate, substances naturally found in articular cartilage, can be taken as nutritional supplements. Although patient reports indicate that these supplements may relieve pain, there is no evidence to support the use of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate to reduce or reverse the progression of arthritis.
Treatments such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell injections involve taking cells from your own body and reinjecting them into a painful joint. PRP uses platelets, a component of your own blood, that are separated from your blood, concentrated, and injected into your knee. Platelets contain “growth factors” that are thought to help reduce signs of inflammation.
Stem cells are precursor cells that can also be taken from your own body and injected into your knee. Because they are basic cells, they may have the potential to develop into new tissue and thus heal damaged joint surfaces.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
If your pain from arthritis is causing disability and is not relieved by nonsurgical treatment, your doctor may recommend surgery. As with all surgery, there are some risks and possible complications with different knee procedures. Your doctor will discuss possible complications with you before surgery.
arthroscopy:
During arthroscopy, doctors use small incisions and thin instruments to diagnose and treat joint problems.
Osteotomy:
A knee osteotomy may be performed when you have early-stage osteoarthritis that damages only one side of the knee joint. An osteotomy can relieve pain and significantly improve function in your arthritic knee by shifting your weight from the damaged side of the joint.
Full or Partial Knee Prosthesis (Arthroplasty):
Your doctor will remove the damaged cartilage and bone and then insert new metal and/or plastic joint surfaces to restore the function of your knee.
HEALING PROCESS
There is a recovery period after any type of surgery for knee arthritis. Recovery time and rehabilitation depend on the type of surgery performed.
Your doctor may recommend physical therapy to help you regain strength and range of motion in your knee. Depending on your procedure, you may need to wear a knee brace or use crutches or a cane for a while.
In most cases, surgery relieves pain and makes it possible to perform daily activities more easily.
Op. Dr. Barış PEKER
orthopedics and Traumatology specialist
Contact Us For Appointment:
Telephone line: 0392 444 3548 (ELIT)
Contact Form: https://www.elitenicosia.com/iletisim/