West Nile Virus

Definition:
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes West Nile fever. It is a member of the Flaviviridae family, in the genus Flavivirus, which also includes Zika, dengue, and yellow fever viruses.
From where:
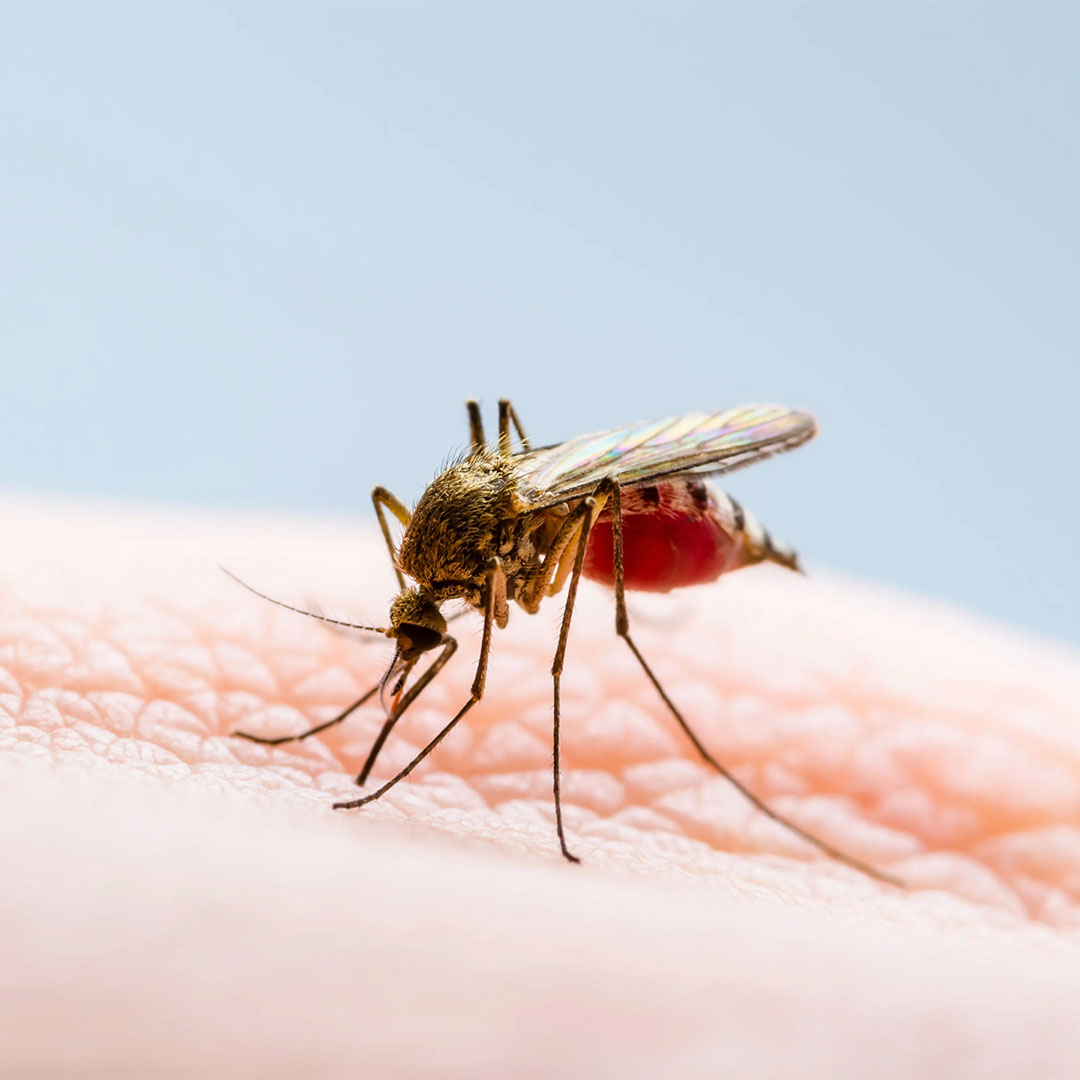
The virus is transmitted by mosquitoes. The primary hosts are birds, so the virus remains in a “bird-mosquito-bird” transmission cycle.
It is transmitted to humans mostly through the bite of an infected mosquito. It continues especially in summer and until autumn.

Symptoms:

Most people (8 out of 10) do not develop any symptoms.
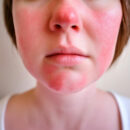
About 1 in 5 people develop a fever along with other symptoms such as headache, abdominal pain, body aches, joint pain, vomiting, diarrhea, or rash. Most people with febrile illness recover completely in 3-6 days, but fatigue and weakness may last for weeks or months.
About 1 in 150 people develop a serious disease affecting the central nervous system, such as meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord). or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
Symptoms of severe disease include high fever, headache, stiff neck, disorientation, coma, tremors, convulsions, muscle weakness, lethargy and paralysis, and are more common in people over 60 years of age, chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, weak immune system, cancer. It can be seen in people with diseases.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is often made by the doctor examining the patient's signs and symptoms, keeping in mind that most WNV-infected patients will develop a skin rash!
Possible history of exposure to mosquitoes that can carry West Nile virus.
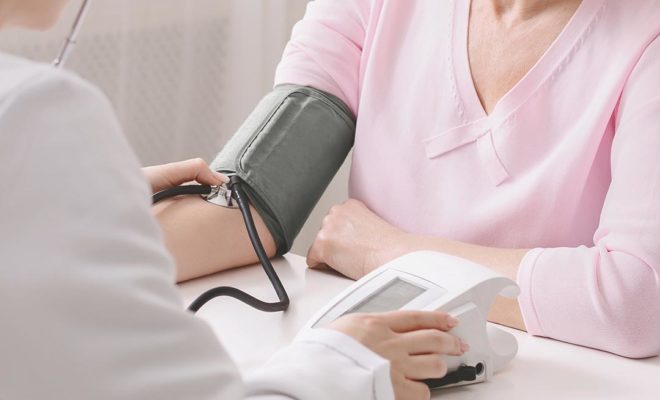
Laboratory tests on blood (CBC and CRP) or spinal fluid to check for Ig-M antibodies to the virus.
Brain CT and Brain MRI may be needed in cases of meningitis and encephalitis.
NOTE: Symptoms of West Nile virus infection are similar to symptoms of other viral infections. There may be no specific findings in the patient's physical examination!
Treatment:
There is no vaccine or specific medication available against West Nile virus infection. Remember that antibiotics do not cure viruses!!!
Bed rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain medications (Ibuprofen and acetaminophen, vitamin C and vitamin D) may relieve some symptoms.
In severe cases, patients may need to be hospitalized to receive supportive treatment such as intravenous fluids, painkillers, and nursing care to reduce the risk of developing complications.
Immunity and prognosis:
People with mild West Nile virus infection recover after treatment.
Most people infected with West Nile virus are believed to have lifelong immunity against contracting the disease again.
Prevention:
The best way to prevent this is to avoid mosquito bites.
Using mosquito repellent products containing DEET (N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide).
Wear long sleeves and pants.
Draining stagnant water in pools (mosquitoes breed in stagnant water).
Community spraying for mosquitoes can also reduce mosquito breeding.
Dr. Ali Al Sahli
Elite Hospital Emergency Service
Contact Us For Appointment:
Telephone line: 0392 444 3548 (ELIT)
Contact Form: https://www.elitenicosia.com/iletisim/