Healthy Weight Control

Losing weight should not be seen as a goal in itself, but as a tool for a healthier life. It is a known fact that overweight people have higher cardiovascular risks and health problems such as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome are more common. In addition to improving our appearance while losing weight, becoming healthier biologically and physiologically is an important goal for us.
If you do not have enough knowledge about weight control and healthy nutrition, it is very important to get help from a nutritionist. In addition, let's take a look at some methods that can be applied to healthy eating and weight loss:
General Nutrition Recommendations
There are three types of macronutrients that are essential for human health. These are called carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Our body also needs all macromolecules. Therefore, restrictive diets such as ketogenic and Dukan diets may have negative consequences on health in the long term. It is considered appropriate for an average adult's daily nutrition to be as follows:1:
Carbohydrate: 45-65%
Protein: 10-35%
Oil: 20-35%
When we think of carbohydrates, we usually think of foods such as bread, pasta and rice, but vegetables, legumes and many other foods are very rich in carbohydrates. The difference is that carbohydrate foods such as sugar, bread, rice and pasta have a high glycemic index, and carbohydrate foods such as vegetables and legumes have a lower glycemic index. The glycemic index shows how quickly a food turns into sugar and enters the blood. Since foods with a high glycemic index will rapidly increase sugar and subsequently insulin levels, they will have negative effects in cases of insulin resistance, reactive hypoglycemia and type 2 diabetes. It is especially recommended for people with insulin resistance, diabetes or reactive hypoglycemia to consume foods with a lower glycemic index.2.
The healthy fats that our body needs are mostly omega-3 and omega-6 fats. These oils, found in foods such as fish, olive oil, avocado and banana, should be a part of our nutritional ritual. However, animal fats and margarines with high saturated fat content should not be included in our daily food consumption.
Intermittent Fasting (Restricted Nutrition)
Fasting is a nutritional approach that alters eating and hunger periods. It has gained popularity in recent years due to its numerous health benefits. There is a habit of fasting for various reasons in many cultures and religions. For this reason, fasting is a subject that has been examined and researched scientifically. Here are the main advantages of fasting3,4,5:
1. Weight Management: Intermittent fasting helps with weight loss and weight management. By restricting the eating window, the body uses stored fat for energy during fasting periods, resulting in a decrease in total calorie intake. In clinical studies, it has been observed that many health indicators are better in people who consume food only within a certain period of time by intermittent fasting instead of spreading their meals throughout the day, even though the amount of food eaten during the day is equal.
2. Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Fasting has been shown to increase insulin sensitivity, which reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes and helps balance blood sugar levels.
3. Cellular Repair and Autophagy: Fasting triggers a process called autophagy, in which the body removes damaged cells and produces new cells. This supports cellular repair and may have anti-aging effects.
4. Heart Health: Studies show that fasting may lower LDL cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and other risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
5. Increased Metabolism: Fasting can increase metabolic rate and increase the body's capacity to burn calories efficiently.
6. Reduced Inflammation: Fasting can reduce inflammation in the body, which is associated with several chronic diseases, including arthritis and some cancers.
7. Longevity: Some animal studies suggest that fasting may extend lifespan, but more research in humans is needed to fully understand this effect.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional before you begin fasting, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or concerns. Remember that fasting may not be suitable for everyone and individual results may vary. For long-term success, it's important to find an approach that suits your lifestyle and preferences. If you are a person who is used to eating 3 meals a day, it will not be easy to suddenly switch back to eating one meal a day. Therefore, personalized goals should be determined.
Semaglutide Injection
The injection called Semaglutide is a drug within the scope of glucagon-like peptide, that is, GLP-1 analogue. You may also know this drug by its trade names: Ozempic or Wegovy.
Semaglutide injection, which has made a name for itself with its recent success in appetite control and weight loss, has gained serious demand because it is administered once a week and its side effect profile is quite innocent.
This drug basically has certain effects. These are the main6,7,8:
- Appetite control and decreased interest in food and drinks
- After eating, the passage of food from the stomach to the intestine slows down and therefore the feeling of fullness in the stomach lasts longer than normal.
- By balancing the dopamine level in the brain, some foods and drinks that our brain perceives as rewards do not provide the same pleasure.
This last item is actually very important because the biggest complaint of most of my patients is the desire to eat even if they are full and the pathological level of food consumption. The ability of this drug to regulate this pathological condition coming from the brain also prevents "binge eating disorder", also called binge eating or binge drinking, or the situation of unlimited eating or drinking.
People who will benefit from this treatment can be mainly grouped as follows:
– People with eating disorders and an unhealthy relationship with food
– People with large portions and above-normal food intake
– People with insulin resistance
– People who consume excessive alcohol and develop health problems related to this
Recently, America's Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of this drug for those over 12 years of age. In other words, it is appropriate to treat children with weight and eating problems before this problem gets worse.
Before starting treatment, certain tests must be performed and treatment must be applied accordingly. Applying this treatment on your own without consulting a physician and undergoing certain tests may have negative consequences. After all, it is a medicine to be used and the dose and duration of use must be designed individually.
Metabolism Accelerator and Fat Burning Treatments
The biggest problem of some of our patients is that their metabolic rate is slow and they cannot lose weight even though their portions are small. The complaint of such patients is that they cannot lose weight despite dieting and paying attention to their calorie intake. In such cases, appetite suppressant treatments may not have the desired effect, and as additional support, it can be aimed to accelerate metabolism and reduce inflammation in the body.
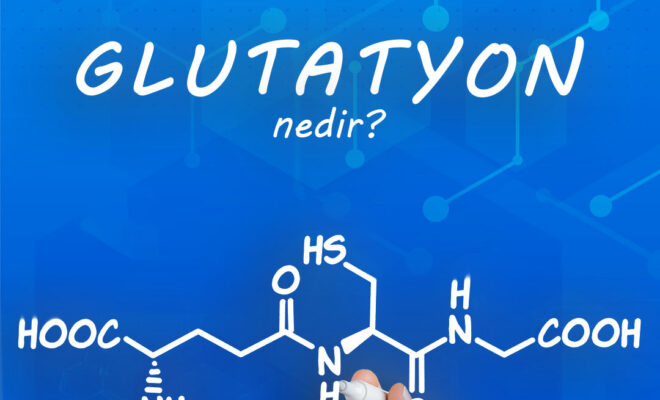
Weight loss can be accelerated by triggering cellular energy production, reducing inflammation in the body and reducing insulin resistance. The most important of these treatments are NAD, Glutathione, Ipamorelin, CJC-1295, MOTS-c and Quercetin.
References
1. Kehoe, L. et al. (2021) 'Energy, macronutrients, dietary fiber and salt intakes in older adults in Ireland: Key sources and compliance with recommendations', Nutrients, 13(3), p. 876. doi:10.3390/nu13030876.
2. Jenkins, D.J. et al. (2002) 'Glycemic index: Overview of implications in health and disease', The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 76(1). doi:10.1093/ajcn/76.1.266s.
3. Vasim, I., Majeed, CN and DeBoer, MD (2022) 'Intermittent fasting and Metabolic Health', Nutrients, 14(3), p. 631. doi:10.3390/nu14030631.
4. Song, D.-K. and Kim, Y.-W. (2023) 'Beneficial effects of intermittent fasting: A narrative review', Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science, 40(1), pp. 4–11. doi:10.12701/jyms.2022.00010.
5. Longo, V.D. et al. (2021) 'Intermittent and periodic fasting, longevity and disease', nature aging, 1(1), pp. 47–59. doi:10.1038/s43587-020-00013-3.
6. Aranäs, C. et al. (2023) 'SEMAGLUTIDE reduces alcohol intake and relapse-like drinking in male and female rats', eBioMedicine, 93, p. 104642. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104642.
7. Nicolau, J. et al. (2022) 'Short term effects of semaglutide on emotional eating and other abnormal eating patterns among subjects living with obesity', Physiology & Behavior, 257, p. 113967. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2022.113967.
8. Zhong, P. et al. (2022) 'Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: A meta-analysis', endocrine, 75(3), pp. 718–724. doi:10.1007/s12020-021-02945-1.