Pre-Diabetes (Hidden Sugar)

What is Pre-diabetes (Hidden Diabetes)?
Pre-diabetes, popularly known as prediabetes, is defined as a person's fasting blood sugar being above normal, but not high enough to diagnose diabetes.
What tests determine whether you have pre-diabetes?
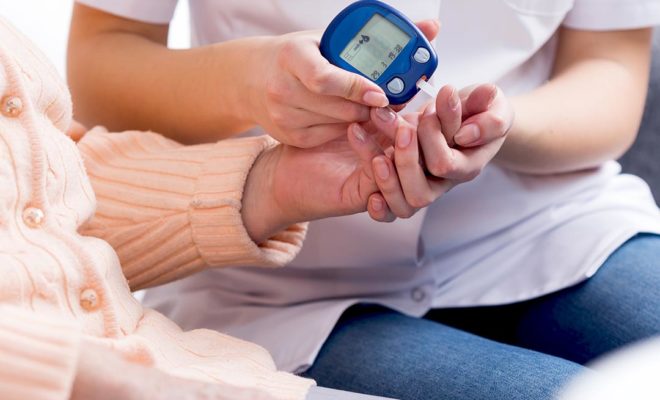
Fasting blood sugar or oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is used to identify pre-diabetes. An overnight fast is required for both tests. For fasting blood sugar, blood sugar is measured after fasting for at least 8 hours before having breakfast. In OGTT, blood sugar is measured again 2 hours after fasting and after drinking a glucose-rich drink.
How is Diabetes or Pre-diabetes determined based on fasting blood sugar values?
Normally, fasting blood sugar is below 100 mg/dl. If a person has pre-diabetes, fasting blood sugar is between 100-125 mg/dl. If blood sugar is 126 mg/dl or higher, the individual has diabetes.
How is Diabetes or Pre-diabetes detected with OGTT?
In OGTT, an individual's blood sugar is measured after fasting and 2 hours after drinking a glucose-rich drink. Normal blood sugar is below 140 mg/dl at 2 hours. If the 2nd hour blood sugar is between 140-199 mg/dl, pre-diabetes is diagnosed, and if the 2nd hour blood sugar is above 200 mg/dl, diabetes is diagnosed.
Are pre-diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose or Impaired Glucose Tolerance the same thing?
Yes. Impaired fasting glucose is defined as fasting blood sugar between 100-125 mg/dl. Impaired glucose tolerance is defined as OGTT 2nd hour blood sugar being detected between 140-199 mg/dl. While only impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance is detected in some people, both conditions are observed together in some people.
Why is pre-diabetes important?
Pre-diyabetik hastalar diyabet adayıdır. Pre-diyabetin erken tanısının önemi, hastaya diyabetik olma riskini azaltma veya önleme fırsatı tanımasıdır. Çalışmalar, pre-diyabetik kişide izole bozulmuş açlık glukozu bulunması halinde takip eden 10 yıl içinde diyabet gelişme riskinin %10-15; izole bozulmuş glukoz toleransı bulunması halinde ise riskin %35 düzeyinde olduğunu gostermektedir. Pre-diyabetin en önemli özelliği bu evrede kalp-damar hastalıkları riskinin sağlıklı bireylere göre 1.5 kat artmış olmasıdır. Uygun tedavi ve yaşam tarzı değişikliği ile pre-diyabetiklerin % 60’a yakınında diyabet önlenebilmektedir.
Who should be screened for pre-diabetes?
- obese people
- Those with diabetes in the family
- Those with a history of gestational diabetes
- Those with hypertension
- Those who gave birth to babies weighing over 4 kg
- Those with low HDL-cholesterol and high triglyceride levels
- Those with previous glucose intolerance or impaired fasting glucose or metabolic syndrome
- Those with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Those receiving antipsychotic treatment for schizophrenia or bipolar disorder
- Those with a sedentary lifestyle
- Those over the age of 45 should be screened for prediabetes.
How should pre-diabetes treatment be?
When pre-diabetes is diagnosed, the first recommendation is serious lifestyle change. A series of regulations, from increasing daily activity to nutritional habits, are gradually implemented. Obese pre-diabetic patients should lose at least % 5-10 of their weight and maintain their new weight in the long term. If there is no objection, moderate physical activity lasting 30-60 minutes at least 5 days a week is recommended. A diet as low in salt and alcohol as possible is appropriate. Since weight loss has a very important effect on preventing the development of diabetes, obese people can be supported with medication to lose weight when necessary.
Yaşam tarzı değişikliklerinin önemini gösteren en önemli çalışmalardan biri olan Finlandiya Diyabet Önleme Çalışmasında toplam 522 prediyabetik hasta çalışmaya katılmış. Hedef; beden ağırlığının en az %5’i kadar kilo kaybı, günlük total yağ alımının kısıtlanması, diyette lif alımının arttırılması (en az 15 gr/1000 kalori) ve fiziksel aktivitenin arttırılması (günde en az 30 dakika orta şiddette egzersiz) idi. 3,2 yıllık izlem sonunda kontrol grubunda diyabet gelişimi %23, yaşam tarzı değişiklikleri uygulanan grupta ise %11 saptandı. Bu çalışmanın sonuçlarından biri de diyabet gelişimi için yaşam tarzı değişiklikleri görece olarak %58 risk azalması sağlamaktadır. Bu çalışma bize , pre-diyabetik kişilerde sadece yaşam tarzı değişikliğinin bile ileride diyabet gelişimini önlemek adına önemli ölçüde katkı sağladığını göstermektedir.
According to the latest data, %8.3 of the world's population is diabetic and %6.9 is a candidate for diabetes, that is, pre-diabetic. These data alone reveal how big a health problem diabetes and pre-diabetes are. Therefore, it concerns such a wide range of people and is very important because of the chronic kidney damage it causes, the increased risk of heart attack and other organ damage it causes by disrupting the structure of the vessels, and the cost it creates for the states. Preventing such a major health problem before it even starts, that is, detecting the person when he is pre-diabetic and giving appropriate treatment is of vital importance in eliminating health problems that people who are candidates for diabetes may experience in the future and may result in death.
Dr. Sabiha Gökçen Asvaroğlu
Internal Medicine Specialist
Contact Us For Appointment:
Telephone line: 0392 444 3548 (ELIT)
Contact Form: https://www.elitenicosia.com/iletisim/