Colon (Large Intestine) Cancer Awareness Month
COLUMN CANCER AWARENESS MONTH
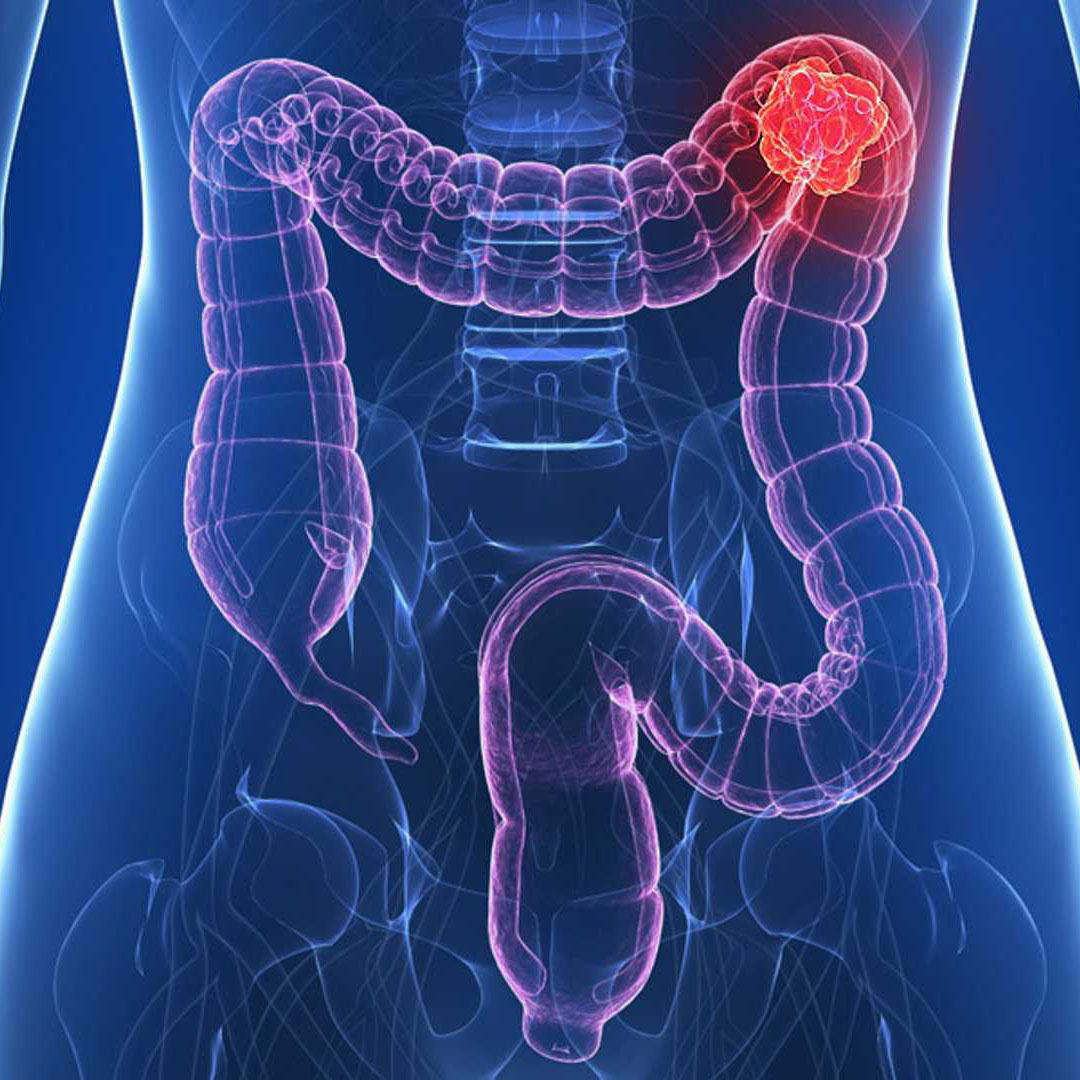
Colon cancer is cancer of the large intestine, which is the last part of the digestive system. It ranks 3rd among cancer-related causes of death worldwide. However, satisfactory results can be achieved thanks to screening tests and early diagnosis. Thanks to today's advanced surgical and medical treatments, the 5-year survival rate in patients diagnosed early has increased above 90%'s.
What are the Risk Factors?
- interchangeable
- Being overweight or obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Diet rich in red meat and processed meats
- Smoking and alcohol use
- diet low in fiber
- unchangeable
- advanced age
- Family history of colorectal polyps or cancer
- Having inflammatory bowel disease (Ulcerative colitis or Crohn's)
- hereditary cancer syndromes such as Lynch and FAP
- Type 2 Diabetes
What are the symptoms and signs?
– Abdominal pain, indigestion, bloating
– Change in bowel habits and stool pattern
– Increase in the number of defecation
– Bloody stools
– Constipation
– Anemia
– Weight loss and fatigue
Diagnosis
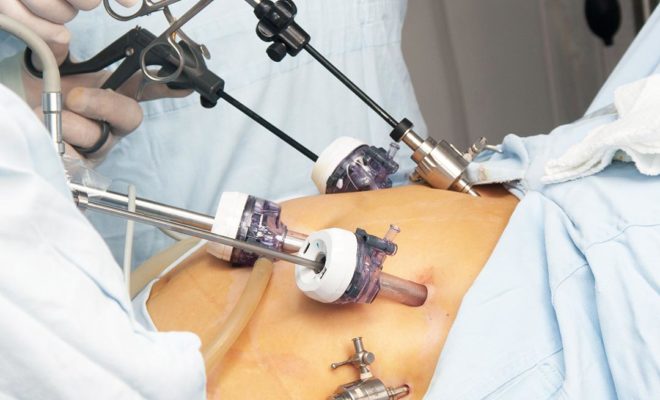
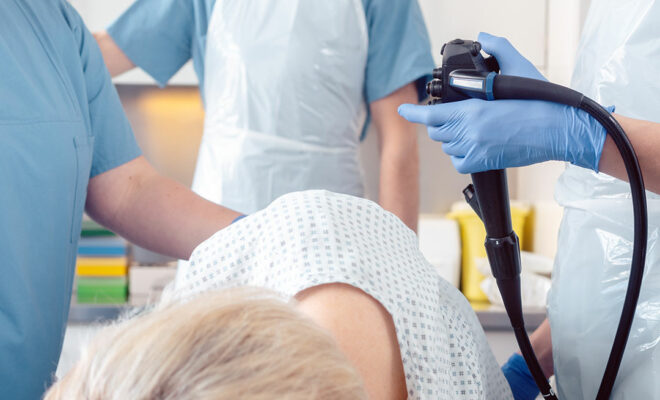
The most important tool in diagnosis is colonoscopy. The inner surface of the entire large intestine can be examined in detail with a colonoscope. In addition, polyps can be detected and removed with colonoscopy before cancer develops.
Blood tests (cancer antigens such as CEA and CA 19-9, etc.), Computed Tomography and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) are used as other diagnostic methods.
Screening Tests
FOBT (Fecal occult blood) and colonoscopy are used in colon cancer screening. It is recommended that every individual undergo a colonoscopy every 5 years and a FOBT test once a year, starting from the age of 50. Colonoscopy is recommended every 2 years in patients with family history and risk factors.
Treatment Methods
Colon cancer is one of the most treatable cancers when diagnosed and treated in its early stages. The treatment protocol for colon cancer is generally aimed at increasing the patient's life expectancy and quality. Polyps with cancer-causing potential are usually removed and treated by colonoscopy. The first treatment option for early stage colon cancer is surgery to remove the diseased part of the intestine. In more advanced stage colon cancers that have metastasized (spread) through the lymph and vessels, the tumor is generally expected to shrink with treatments such as chemotherapy, and then surgery is performed.
What can be done to reduce the risk of colon cancer?
- Cancer Screening
- Screening tests (fecal occult blood and colonoscopy) should be performed starting from the age of 50 in people who do not have a family history of cancer. In those with a family history of inflammatory bowel diseases and colorectal cancer syndromes, screening tests should be started at an earlier age.
- Lifestyle Change
- Eating a diet rich in vegetables, fruits and grains, quitting or restricting alcohol and cigarette consumption, and exercising regularly reduces the risk of colon cancer.
Op. Dr. Cemal Seyhun
General surgery specialist
Contact Us For Appointment:
Telephone line: 0392 444 3548 (ELIT)
Contact Form: https://www.elitenicosia.com/iletisim/